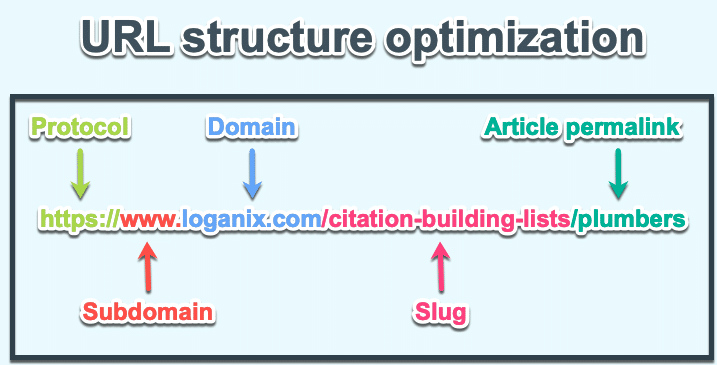
Google Search Console is an essential tool for any digital marketer or website owner.
Whether you’re managing a blog, an eCommerce site, or a corporate page, leveraging the full potential of Google Search Console (GSC) can dramatically enhance your site’s SEO performance.
You can get a report on Discover traffic from Google Search Console. This report will tell you how often your site shows up in users’ Discover, how much traffic you get, and how your content does in Discover compared to regular search results.
You can also find out about Search performance, Index coverage, Mobile usability, Security problems, and Crawl errors from Google Search Console.
In 2024 or beyond, mastering this tool will be more important than ever.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the most advanced features and show you how to use Google Search Console like a pro.
Table of Contents
ToggleAdding Your Website to Google Search Console
Before you can start leveraging Google Search Console (GSC), the first step is to add your website to the platform.
This is a straightforward process but crucial for enabling Google to track your site’s data.
Steps to Add Your Website to Google Search Console
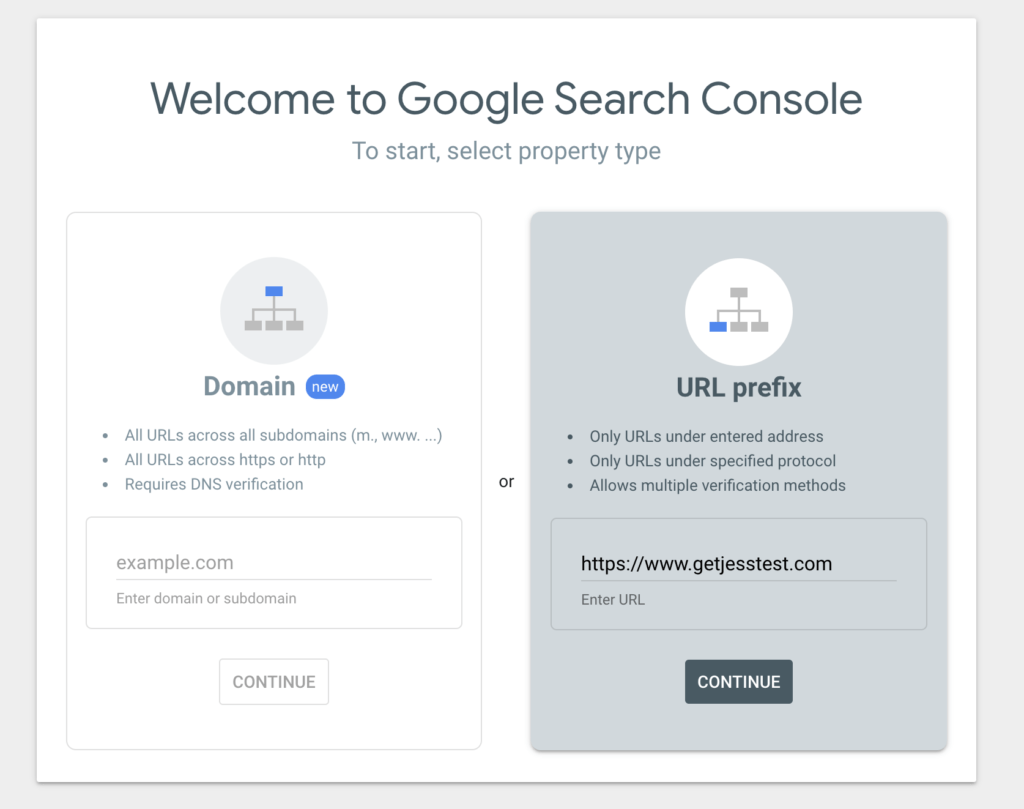
Sign in to Google Search Console: Head over to the official GSC platform and sign in using your Google account.
Add a Property: Once you’re logged in, click on the “Add Property“ button. You’ll have two options: enter your domain name or use the URL prefix. We recommend using the domain property option, as it covers all variations of your site (e.g., www and non-www, HTTP and HTTPS).
Verify Ownership: Google offers several verification methods:
HTML Tag: Add a meta tag to your site’s homepage.
Google Analytics: If you’re already using Google Analytics, you can verify ownership through this integration.
Domain Name Provider: This method verifies ownership through your domain provider (like GoDaddy or Namecheap). Choose the method that works best for you, and complete the process.
Once your website is verified, you’ll have full access to all the data and features Google Search Console offers.
Setting Up Owners, Users, and Permissions
Managing owners, users, and permissions within Google Search Console is essential, especially if multiple team members are involved in maintaining your website.
GSC allows you to control access and assign different levels of permissions to ensure the right people have the correct level of control.
Types of Permissions in Google Search Console
Owner: An owner has full control over the property in GSC. They can add or remove users, adjust settings, and access all data.
Full User: A full user can view all data and take most actions within the console, but they cannot manage other users or settings.
Restricted User: A restricted user has read-only access. They can view most of the data, but they cannot make any changes to the property or its settings.
How to Set Up Users and Permissions
Go to the “Settings“ section in your Search Console dashboard.
Click on “Users and Permissions.”
Add new users by entering their email address and assigning them a role (either full or restricted access).
For owners, this must be done via verification—additional ownership verification methods can be assigned.
This setup allows you to ensure your SEO team, web developers, or stakeholders have the appropriate access to make the necessary updates and changes.
Submitting a Sitemap
One of the first things you should do after adding your website to Google Search Console is submit your sitemap.
A sitemap is essentially a roadmap for search engines to understand your website’s structure, helping them crawl and index your pages more efficiently.
How to Submit Your Sitemap in Google Search Console
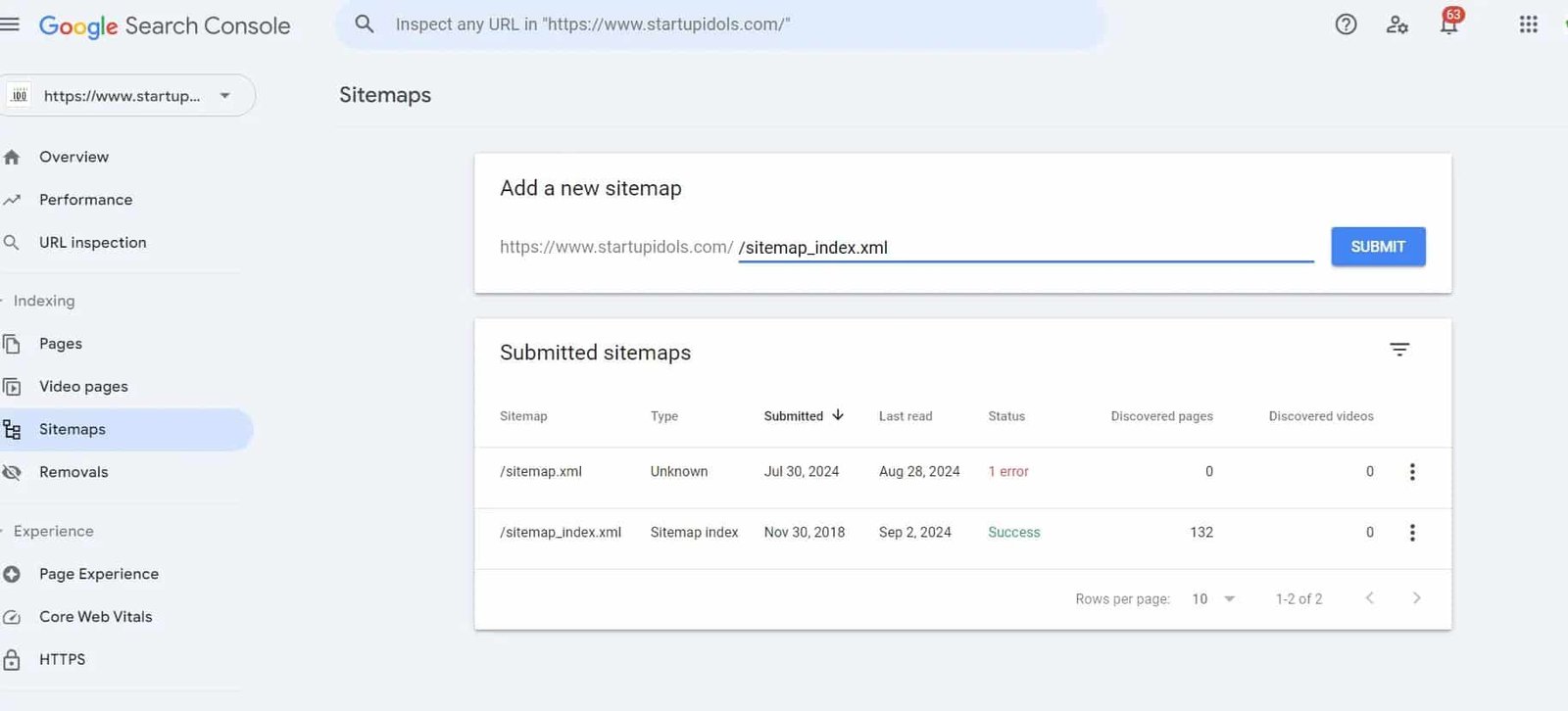
Navigate to the “Sitemaps“ section in your GSC dashboard.
In the “Add a new sitemap” field, enter the URL of your sitemap (usually www.yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml).
Click “Submit.”
Submitting a sitemap ensures that Google can crawl your site more effectively, allowing all of your important pages to be indexed faster and improving your chances of ranking higher in search results.
Best Practices for Sitemaps
Update your sitemap regularly: If you frequently add new content or pages to your website, make sure your sitemap is updated to reflect these changes.
Submit multiple sitemaps if necessary: For large websites with thousands of pages, it’s a good idea to break your sitemap into smaller chunks. GSC allows you to submit multiple sitemaps for better crawlability.
Understanding Dimensions and Metrics
Dimensions in GSC
Dimensions are categories that you can use to break down the performance data. Some of the most useful dimensions include:
Queries: The search terms users typed in to find your site.
Pages: The specific URLs on your website that appeared in search results.
Countries: Data segmented by user location.
Devices: How users accessed your site, whether from desktop, mobile, or tablet.
By analyzing both metrics and dimensions, you can gain detailed insights into which pages and keywords are driving the most traffic and adjust your SEO strategy accordingly.
Key Metrics in Google Search Console
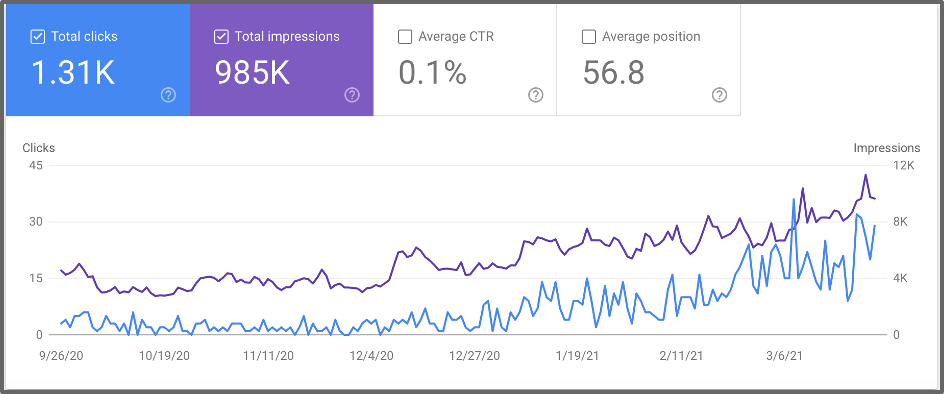
Clicks: The number of times a user clicked on your site from Google’s search results.
Impressions: How often your site appeared in the search results, regardless of whether it was clicked.
Average CTR (Click-Through Rate): This shows the percentage of impressions that resulted in a click. It’s a good indicator of how compelling your title tags and meta descriptions are.
Average Position: The average ranking position of your site for specific keywords. This is a crucial metric to track as you work on improving your site’s SEO.
Adding Filters for Advanced Analysis
Using filters in Google Search Console allows you to zero in on specific data and analyze your performance more thoroughly.
Filters help you refine your reports to focus on key metrics like traffic from a particular country, device, or search query.
How to Add Filters in Google Search Console
Open the Performance Report.
At the top, you’ll find various filter options, such as Query, Page, Country, and Device.
Select the dimension you want to filter by, and GSC will adjust the report to show data based on that filter.
Useful Filters to Consider
Device Filter: Analyze how your site performs across different devices. This can help you spot issues with mobile usability or areas where desktop traffic is outperforming mobile.
Query Filter: Focus on specific queries to understand which search terms are bringing in the most traffic. This is particularly helpful when optimizing for specific keywords.
Date Range Filter: Use this filter to compare performance over different time periods. For example, you can analyze the impact of recent SEO changes by comparing the current month’s data to the previous one.
Best Practices for Setting Up Search Console
Make sure that every version of your site (with and without www, as well as http and https) is added to GSC.
You can consolidate all the data into one view by using domain properties.
This ensures you have a complete picture of how your site performs across all variations.
Key Metrics You Should Focus On
Clicks: The number of times users clicked through from search results to your website.
Impressions: How many times your website appeared in the search results.
Average CTR (Click-Through Rate): The percentage of impressions that resulted in a click.
Average Position: Your website’s average ranking position for all queries.
By analyzing these metrics, you can gain insights into which keywords are driving traffic and identify areas where you can optimize further.
How to Leverage Keyword Data
Use the “Queries“ tab to discover which search terms are bringing users to your site.
Sort by clicks to identify your most valuable keywords and look for terms with high impressions but low click-through rates.
These are often opportunities where tweaking your meta descriptions or title tags could yield significant traffic improvements.
Coverage Report: The Key to Identifying Issues
The Coverage Report in GSC will show you which of your URLs are indexed and which are not. Here’s what to focus on:
Errors: Pages that Google attempted to index but encountered a problem.
Valid with Warnings: Pages that are indexed but may have issues worth investigating.
Excluded: Pages that were intentionally or unintentionally excluded from indexing.
Fixing Common Indexing Errors
404 Errors (Not Found): If Google can’t find a page on your site, it returns a 404 error. These can damage your SEO. Regularly check your GSC for 404s, and redirect these pages to relevant content using 301 redirects.
Crawled – Currently Not Indexed: This issue usually occurs when Google has visited the page but decided not to index it. You might need to update your content, improve internal linking, or address duplicate content issues.
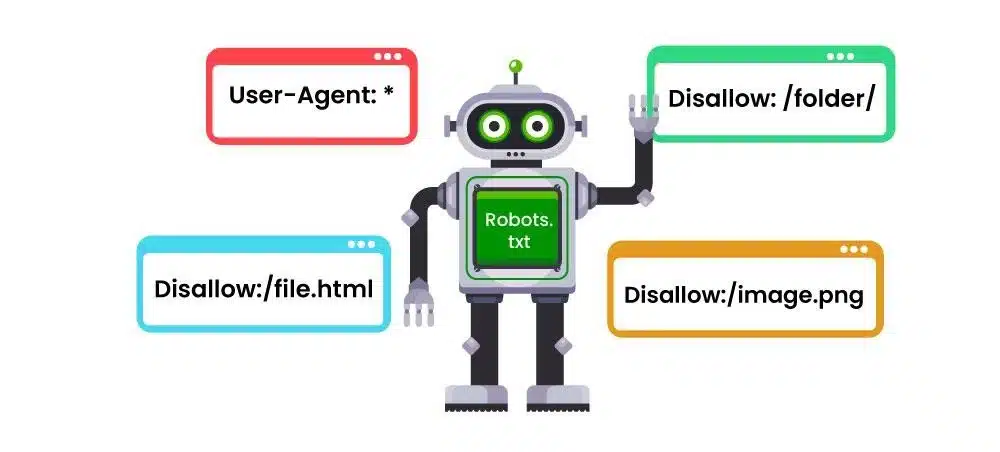
Submitted URL Blocked by Robots.txt: If you accidentally block important pages in your robots.txt file, they won’t be indexed. Double-check that critical URLs aren’t being blocked.
How to Improve Core Web Vitals in GSC
Google Search Console provides a Core Web Vitals Report, which shows you where your pages are performing well and where improvements are needed.
Focus on fixing pages with “Poor” or “Needs Improvement” labels. Consider lazy-loading images, optimizing JavaScript execution, and minimizing CSS to enhance your page speed.
Optimizing Your Website for Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals continue to play a significant role in how Google ranks your site.
These are three specific performance metrics that measure user experience:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): This measures how long it takes for the largest content element on your page to load. Aim for under 2.5 seconds.
First Input Delay (FID): Measures the time it takes for your page to become interactive. The ideal is less than 100ms.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures the visual stability of your page. Keep it below 0.1 to avoid ranking penalties.
Using URL Inspection Tool for Troubleshooting
The URL Inspection Tool in Google Search Console is a critical feature for diagnosing specific page issues.
Whether you’ve made updates to a page or want to check its mobile-friendliness, this tool gives you real-time insights.
How to Use It Like a Pro
Test for Live Issues: You can see whether a specific URL is currently being indexed and how Google sees it. This helps you catch any potential SEO issues before they affect your ranking.
Submit for Reindexing: If you’ve made significant updates to a page, use the URL Inspection Tool to request reindexing. This forces Google to revisit your page more quickly than if you wait for its regular crawl.
Mobile Usability Testing: Since Google has moved to mobile-first indexing, it’s crucial that your site works flawlessly on mobile devices. Use the tool to check for any mobile usability issues.
Tracking Backlinks in Google Search Console
Backlinks remain one of the most important ranking factors. Google Search Console allows you to monitor which sites are linking to your pages, the anchor text used, and the top linked pages.
How to Make the Most of Backlink Data
Identify Your Most Linked Pages: These pages likely contain valuable content, making them ideal candidates for further SEO optimization or internal linking.
Review Anchor Text: Check to ensure that the anchor text pointing to your site is relevant and not spammy. Google may penalize links with over-optimized or irrelevant anchor text.
Disavowing Toxic Links: If you notice suspicious or spammy backlinks in your report, consider disavowing them using Google’s Disavow Tool. This will prevent them from negatively affecting your rankings.
Want to Create Profit-Pumping Niche Websites In Just 180 Seconds?
Utilizing the New Features
Google is constantly improving its tools, and 2024 has introduced a few exciting new features to Search Console that can enhance your SEO strategy.
Performance by Device and Location: This new filter lets you drill down into performance data based on the device (mobile, tablet, desktop) and location. Use this data to target specific devices or regions with customized content.
Regex Filters in Performance Reports: You can now use regular expressions (regex) to perform advanced filtering of queries. This is especially useful if you want to track a group of similar queries or exclude certain terms from your data.
Content Ideas Based on Search Trends: GSC now offers AI-powered suggestions for content topics based on trending queries. Use this to align your content strategy with user intent and attract more organic traffic.
Google Search Console Reports and Features
Now, let’s explore the essential Google Search Console Reports that provide in-depth insights into your site’s performance, technical issues, and opportunities for optimization.
Performance Report
The Performance Report shows how your site performs in Google Search.
It includes metrics like clicks, impressions, CTR, and average position, broken down by queries, pages, countries, and devices.
How to Use the Performance Report:
- Track which queries bring the most traffic.
- Analyze which pages have high impressions but low CTR and optimize them.
- Compare how your site performs across devices and countries.
URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool allows you to analyze specific pages on your website and see if Google correctly indexes them.
Key Features of URL Inspection Tool:
- Indexing Status: See whether a URL is indexed or not.
- Mobile Usability: Check if the page is mobile-friendly.
- Coverage Issues: Identify and fix issues preventing the page from being crawled or indexed.
Page Indexing Report
The Page Indexing Report helps you understand which pages of your website are indexed and which are not, along with reasons why certain pages may not be indexed.
How to Use the Page Indexing Report:
- Monitor how many pages are indexed and if any important pages are missing.
- Investigate reasons for non-indexed pages, such as noindex tags, blocked resources, or canonicalization issues.
Sitemaps Report
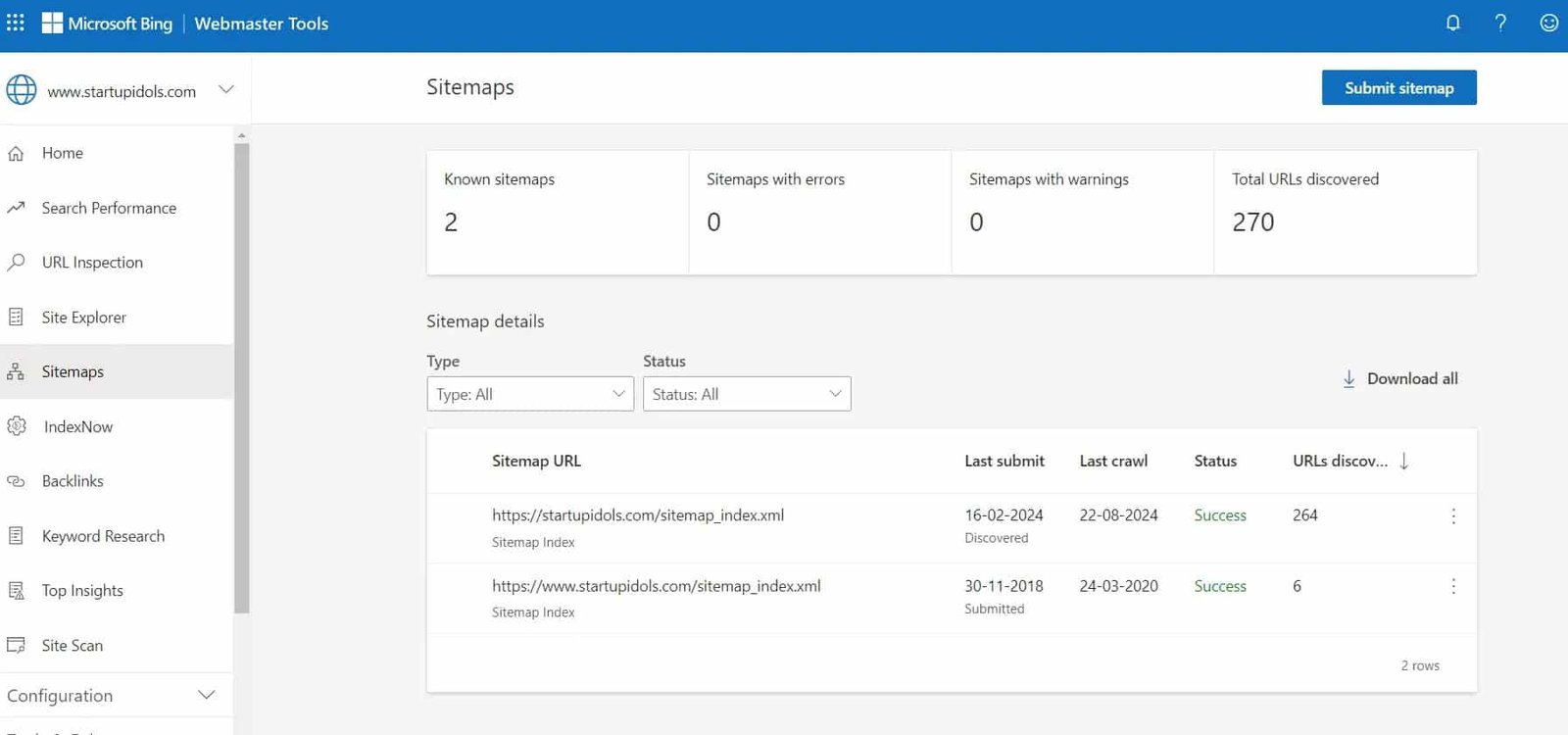
The Sitemaps Report allows you to monitor the status of the sitemaps you’ve submitted to Google.
How to Use the Sitemaps Report:
- Check for errors or warnings that might prevent your sitemap from being crawled.
- Ensure that all important sections of your website are represented in your sitemap.
Page Experience Report
The Page Experience Report evaluates how users perceive the experience of interacting with your web pages. This report is crucial for monitoring Core Web Vitals.
Metrics in the Page Experience Report:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability.
Enhancements Report
The Enhancements Report focuses on structured data and other improvements that can enhance your site’s performance in search results.
Key Features:
- Rich Results: Check if your structured data is correctly implemented to qualify for rich results in search.
- Identify and fix issues related to structured data, such as errors in schema markup.
Manual Actions Report
If your website violates Google’s guidelines, it may be subject to a manual action. The Manual Actions Report shows if your site has been penalized and why.
What to Do if You Receive a Manual Action:
- Address the specific issue flagged by Google, such as unnatural links or thin content.
- Once resolved, submit a reconsideration request through GSC to have the penalty removed.
Links Report
The Links Report provides insights into your site’s internal and external linking structure.
How to Use the Links Report:
- Monitor external links to ensure your site is receiving quality backlinks.
- Analyze internal links to ensure important pages are linked effectively within your website.
Shopping Report
For eCommerce websites, the Shopping Report helps track the performance of your product pages in Google Shopping.
Key Features:
- Identify issues with product data that might prevent items from appearing in Google Shopping.
- Monitor clicks and impressions from product listings to optimize for better performance.
AMP Report
The AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) Report monitors any issues related to your AMP pages, ensuring they load quickly and are mobile-friendly.
How to Use the AMP Report:
- Check for any AMP-related errors or warnings that might affect your pages’ mobile performance.
- Address any issues to ensure your AMP pages provide a fast, mobile-optimized experience for users.
Introducing MAT1 Marketing & Affiliate Training!
A Complete Online Digital Library of Courses To Help You Build Sustainable Predictable Income You Can Rely On Month After Month!
Get AccessConclusion: How to Use Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful tool that provides essential insights into your website’s performance in search results.
By adding your website properly, setting up users and permissions, submitting a sitemap, understanding key metrics, and using filters for advanced analysis, you can unlock this platform’s full potential.
These best practices will help you stay ahead of the competition and continuously improve your site’s SEO performance in 2024.